

As such, reaction slows down and eventually stops. This becomes a protective layer and prevents further reaction of the hydrochloric acid with the underlying lead metal. However, do note that when hydrochloric acid is being used, the initial reaction between lead and hydrochloric acid will form an insoluble layer of lead (II) chloride. Note that lead should react easily with dilute acids since it is higher than hydrogen in the Reactivity Series. Sn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → SnCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts slowly Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts moderatelyįe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts slowly Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts rapidlyĢAl(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl 3(aq) + 3H 2(g) reacts rapidly MetalĢK(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + H 2(g) reacts explosivelyĢNa(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H 2(g) reacts explosivelyĬa(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts violently The reactions of the metals with the dilute acids will also indicate how reactive the metals are and this is used to place them in the Reactivity Series.Ī more reactive metal will react more violently with the dilute acid.Ĭheck out the table below on the observations and chemical equation for the reaction of metals with dilute acid. Metal + Dilute Acid → Salt Solution + Hydrogen Gas

Most metals react with dilute acids to form a salt solution and hydrogen gas. Sn(s) + H 2O(g) → SnO(s) + H 2(g) reacts readilyī) Reaction of Metals with Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Zn(s) + H 2O(g) → ZnO(s) + H 2(g) reacts readilyģFe(s) + 4H 2O(g) → Fe 3O 4(s) + 4H 2(g) reacts slowly Mg(s) + H 2O(g) → MgO(s) + H 2(g) violent reactionĢAl(s) + 3H 2O(g) → Al 2O 3(s) + 3H 2(g) reacts readily Mg(s) + 2H 2O(l) → Mg(OH) 2(aq) + H 2(g) very slow reaction MetalĢK(s) + 2H 2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H 2(g) violent reactionĢNa(s) + 2H 2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H 2(g) violent reactionĬa(s) + 2H 2O(l) → Ca(OH) 2(aq) + H 2(g) reacts readily Note that a more reactive metal reacts violently with steam.Ĭheck out the table below on the observations and chemical equation for the reaction of metals with cold water and/or steam. Metal + Steam → Metal Oxide + Hydrogen Gas Such metals will react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen gas. Some metals such as zinc and iron, do not react with cold water but they do react with steam. Note that a more reactive metal will react more violently with cold water. Metal + Water → Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen Gas This reaction can be easily represented by the following word equation:
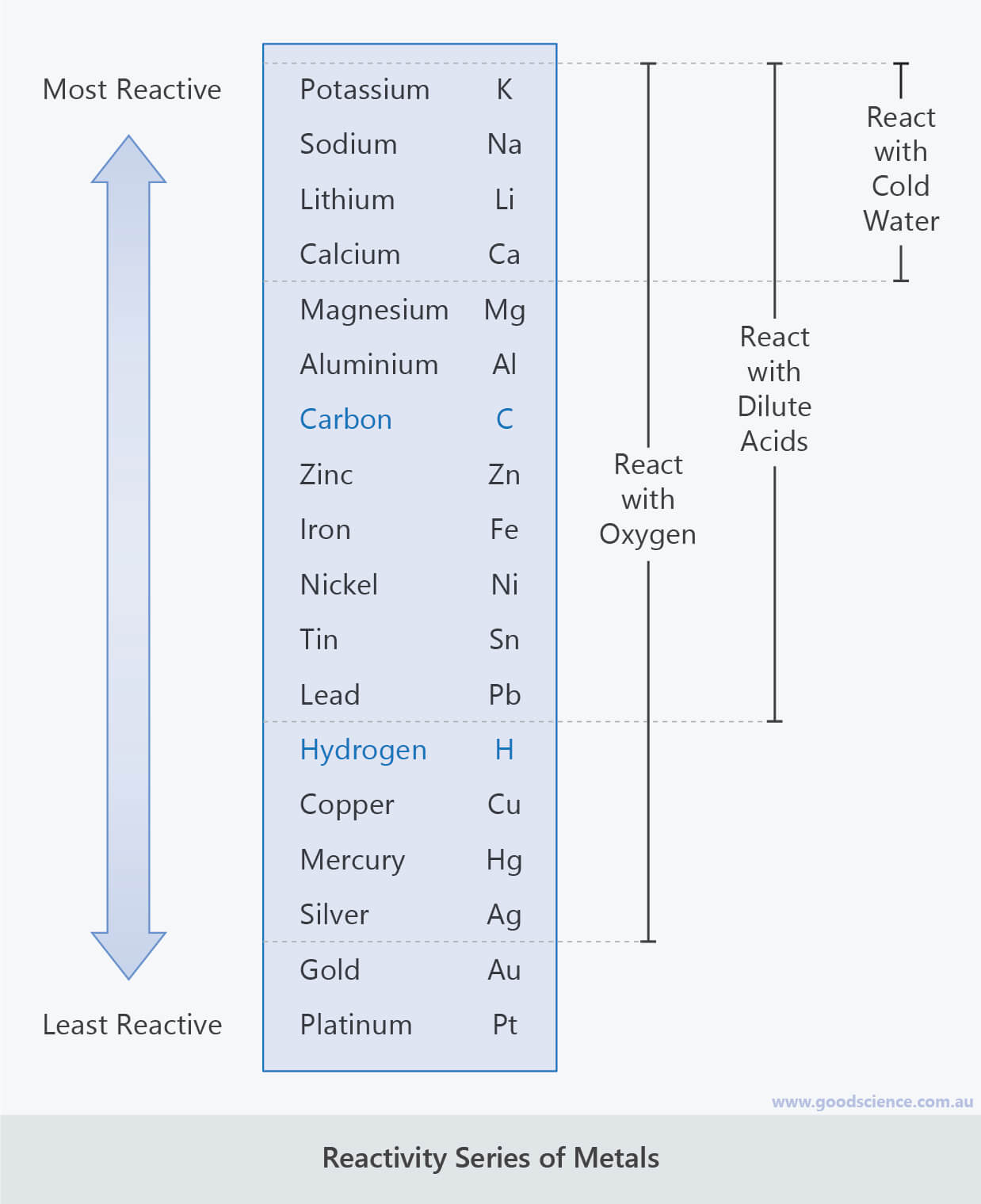
The more reactive metals tend to react with cold water to form metal hydroxide (alkaline solution) and hydrogen gas. Reaction of metals with dilute acids such as hydrochloric acidĭetermining the Order of Reactivity of Metals A) Reaction of Metals with Cold Water or Steam.Reaction of metals with cold water or steam.The order of reactivity of metals are determined by the scientists based on the: So how is the order of reactivity of metals being determined? In the Reactivity Series, metals are arranged from the most reactive to the least reactive. In case you have missed that blog post which comes with a learning Chemistry Youtube Video, do check it out.

In the previous blog post, we have discussed on the importance of the Reactivity Series of Metals as well as the mnemonic (super memory technique) to remember the sequence of metals in terms of their relative reactivities. Source: Science Photo (Reaction of Metals with Hydrochloric Acid)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
